Affordable and Clean Energy
Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all.
Research on SDG7 - Clean Energy
【Research Programs】
SDG7 - Related Research Projects | Department/College/Institute |
Research on the Current Situation, Characteristics and Trends of Energy Supply and Demand in Macau within the Guangdong - Hong Kong - Macao Greater Bay Area | Macau Institute for Environmental Research |
Multi - spectral Vision and Multi - dimensional Precision Detection Technology and Equipment for New Energy Vehicle Motors | FIE-SCSE |
Research Service on the Energy Efficiency Status of the Macau Special Administrative Region in 2023 | TISD |
Systematic Research on Distributed Photovoltaic Systems for Urban - Energy - Sustainability Co - development in the Era of Artificial Intelligence and Its Application in the Guangdong - Hong Kong - Macao Greater Bay Area | FIE-MISE |
Research on the R & D Investment Issues of New Energy Enterprises under Uncertain Grid - connected Electricity Prices | MSB |
【Publications】
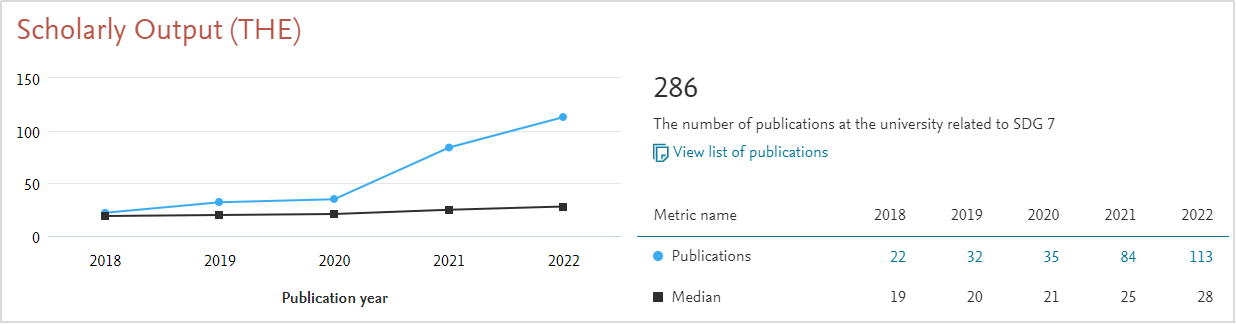
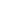
Figure 1 MUST SDG7 Paper Growth Trend
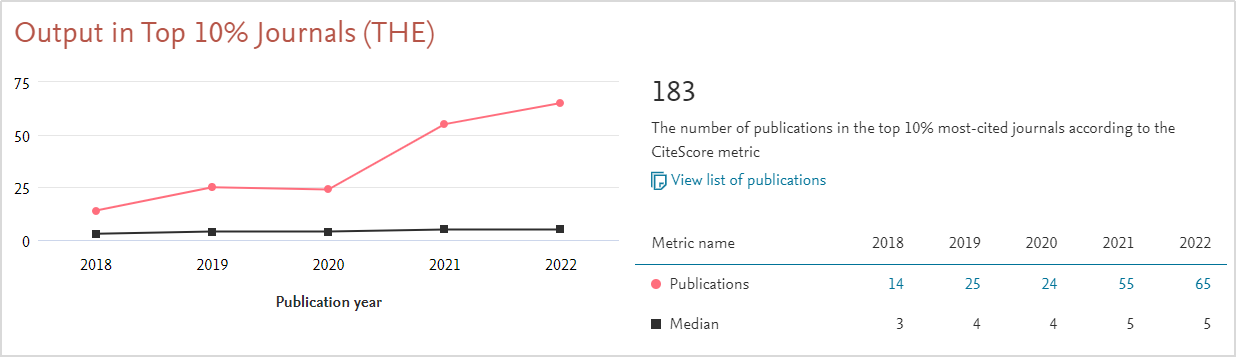
Figure 2 Number of MUST SDG7 Papers Published in Top 10% Journals
University measures towards affordable and clean energy
MUST actively promotes green buildings and environmental protection on campus. It ensures that buildings meet energy - efficiency standards. Taking Building R as an example, the university has formulated plans to improve the energy - efficiency levels of existing buildings to achieve low - carbon and sustainable development. For more details, please refer to https://www.must.edu.mo/id - 13630/article/view/id - 18719.html. To this end, MUST actively promotes carbon management and emission reduction, sets carbon - neutrality goals, and takes measures such as optimizing energy use and promoting green buildings, demonstrating a strong commitment to environmental protection responsibilities (for more details, see https://sust.must.edu.mo/page/green - actions.html). Meanwhile, MUST has developed an energy - efficiency improvement plan to promote energy conservation, emission reduction, and sustainable development. This includes encouraging teachers and students to wear casual clothes to reduce air - conditioning use, optimizing energy use, and promoting green buildings. The university is actively working to reduce overall energy consumption (for more details, see https://www.must.edu.mo/news/45174 - article0606155018). Through regular energy audits, MUST identifies and reduces areas of energy waste, improves overall energy efficiency, and promotes sustainable development. In addition, MUST is committed to sustainable development and environmental protection. By formulating sustainable investment policies, promoting green buildings, investing in the construction of renewable energy facilities, and carrying out relevant research and courses, the university demonstrates its commitment to sustainable development and educates students and society.
Energy Audit Requirements
In accordance with the "Building Energy Audit Operation Code (2024 Edition)" and the ANSI/ASHRAE/ACCA 211-2018 (R2023) Standard for Commercial Building Energy Audits, a comprehensive energy audit for the MUST Building R was completed in October 2024. The audit process included a comprehensive walk-through of the building and a review of related systems and equipment, including installations for central building services such as air conditioning, electrical systems, lighting, elevators, escalators, plumbing, and drainage systems.
Optimizing Energy Management
Through the energy audit, the aim was to assess the current status of the building's energy consumption and identify implementable Energy Management Optimization (EMOs). The goal of these optimization measures is to enhance the building's energy management efficiency and overall energy performance.
Long-term Improvement Measures
Following the energy audit, a series of long-term improvement measures have been formulated to ensure the building's energy efficiency complies with local building energy efficiency regulations. These measures include: 1. Reducing energy consumption and lowering energy costs. 2. Enhancing the reliability and availability of facility systems/equipment: Ensuring the continuous and stable operation of building equipment to avoid energy efficiency losses. 3. Maintaining and upgrading building operational services: Guaranteeing that building operations and management consistently meet good standards, thereby improving overall performance.
Compliance with Energy Efficiency Regulations
These improvement measures ensure that the new building (Block R) can achieve and comply with local building energy efficiency regulatory requirements, aligning with government and industry standards to realize sustainable development benefits.
Macau University of Science and Technology Makes New Progress in Promoting Green and Low-Carbon Development
Research results from the "Construction of Yanpu Bay as a Negative Carbon Bay" project, led by the Macau University of Science and Technology (MUST) Institute for the Study of the Environment, have been certified by the China Quality Certification Centre (CQC). Yanpu Bay has become the first "Negative Carbon Bay" area in China to receive authoritative certification. This achievement was reported on the front page of the China Environment News. The project, supported by the Zhuhai MUST Science and Technology Research Institute, was led by MUST Associate Professor Dong Yahong, with participation from MUST PhD student Zhao Yating and Master's student Tang Chang. It was completed in collaboration with the Key Laboratory of Human and Nature Life Community of Jinan University and the China Quality Certification Centre.
(For details, see: https://www.must.edu.mo/id-13630/article/view/id-31186.html)
Macau University of Science and Technology's Commitment to Promoting Renewable Energy
As a leader in promoting green and low-carbon development, MUST is not only committed to its own green transformation but also actively responds to global climate change challenges, promoting sustainable development for the entire society. The university will actively promote the use of 100% renewable energy in the future through scientific research, technological innovation, and academic exchange. Specific actions include:
1.Comprehensive Electrification:Phasing out fuel-burning equipment on campus and actively promoting the use of electric equipment to reduce the direct burning of fossil fuels at the source and lower carbon emissions.
2.Power Decarbonization:Optimizing the campus power supply structure by gradually increasing the proportion of renewable energy, reducing the carbon intensity of electricity, and providing sustained support for achieving a green, low-carbon campus.
3.Expanding Solar PV Scale: Installing solar photovoltaic panels on a large scale on campus building rooftops and available open spaces to increase the self-sufficiency rate of renewable energy and ensure the sustainability of the university's energy consumption.
(For details, seehttps://sust.must.edu.mo/page/climate-a&p.html?locale=zh_CN)
Energy Use Density
Upgrade/Retrofit Project Plans for the Next 3 Years
Building R at MUST has developed a plan for upgrade/retrofit projects over the next three years for equipment such as the air conditioning system, lighting system, elevators and escalators, and electrical system. The specifics include the following aspects:
1. Air Conditioning System
Over the next three years, the air conditioning system will undergo comprehensive upgrades and optimization, with a focus on improving its energy efficiency. Plans include regular cleaning of air conditioning equipment and haze removal filters to ensure efficient operation. By implementing a maintenance schedule, conducting regular inspections of ducts and equipment, and promptly repairing leaks, the continuous and efficient operation of the air conditioning system will be ensured. Furthermore, the switching status of indoor air conditioning units will be intelligently managed based on the building's usage patterns to avoid unnecessary energy waste, ensuring the system operates optimally in every season.
2. Lighting System
The lighting system will undergo energy-efficient LED retrofitting over the next three years, and the existing lighting control system will be optimized to achieve intelligent adjustment functions, thereby improving energy utilization and reducing consumption. Based on building occupancy, lighting will be turned off when not needed, avoiding unnecessary switching and further reducing electricity waste. Simultaneously, regular cleaning and maintenance of lighting equipment will ensure proper operation and extend its service life. Additionally, plans include reducing the number of lighting fixtures in each restroom through optimized design to further lower energy consumption.
3. Elevators and Escalators
Elevators and escalators will undergo modernization upgrades over the next three years to enhance their operational efficiency and safety while reducing energy consumption. By introducing advanced technologies and equipment, the efficient and stable operation of these systems will be ensured, further improving the building's overall energy efficiency. Moreover, the building will encourage employees and visitors to use stairs for movement between floors, especially for short vertical distances of 1-2 floors, through posters, signs, etc., thereby effectively reducing elevator usage frequency and energy consumption.
4. Equipment Monitoring and Adjustment
All critical facilities will be monitored and adjusted to ensure they are always in optimal operating condition. Over the next three years, the building will perform regular calibration and replacement of equipment, particularly addressing issues such as abnormal sensor readings, flickering lights, excessive fan noise, or air conditioning water leaks by promptly repairing or replacing faulty equipment. These measures will effectively improve equipment operational efficiency, reduce energy waste caused by equipment failures, extend equipment service life, and ensure the efficient and stable operation of building facilities.
5. Electrical System
The electrical system will undergo intelligent upgrades, optimizing load management and enhancing system stability and reliability. By integrating data from digital power analyzers into the Building Management System (BMS) or a new power quality management system, the building will continuously monitor power quality to ensure the efficient operation of the electrical system. These intelligent upgrades will help optimize power consumption, reduce electricity waste, and ensure the stability and reliability of the electrical system in building operations, thereby improving overall energy efficiency.
MUST has already developed and implemented a rational energy efficiency improvement plan, committed to reducing overall energy consumption. Through measures such as optimizing energy use, introducing low-carbon technologies, and promoting the use of green energy, we ensure that the energy efficiency of buildings and facilities reaches an optimal level. Our energy efficiency improvement plan specifically includes the following aspects:
1. Optimizing Existing Energy Use Efficiency:
By regularly inspecting and maintaining existing energy systems, we identify and address energy waste issues, ensuring all types of facilities operate at their highest efficiency.
2. Introducing Intelligent and Low-Carbon Technologies:
Upgrading systems such as air conditioning, lighting, and electrical systems by adopting intelligent control technologies to achieve automatic adjustment and energy optimization. Furthermore, systems will intelligently adjust their operating status based on usage and demand, avoiding energy waste while reducing carbon emissions.
3. Promoting Renewable Energy:
Increasing the use of renewable energy on campus, such as solar power, to reduce reliance on traditional energy sources.
4. Whole-Participation:
Advocating for the active participation of students, faculty, and staff in energy-saving and emission-reduction activities, promoting the development of a green campus culture. Through initiatives like energy conservation awareness training and green action advocacy, we encourage everyone to start with themselves, adopt energy-saving measures in daily life, and collectively create a low-carbon, environmentally friendly campus environment.
Energy and the Community
MUST actively supports the development of startups in the low-carbon economy and technology sectors. By providing support such as financing, technical guidance, and marketing, it establishes an innovation ecosystem to promote sustainable business models, while focusing on corporate social responsibility. MUST believes that low-carbon technology is a crucial direction for the future economy. (Details: https://www.must.edu.mo/en/cecp/startup)
MUST's Energy Policy and Investment Guidelines
MUST has formulated a comprehensive energy efficiency plan aimed at promoting energy conservation, emission reduction, and sustainable development. To reduce energy consumption, MUST has implemented various measures, such as encouraging students and staff to wear casual clothes to reduce air conditioning use, optimizing energy usage, and promoting green buildings, all dedicated to lowering overall energy consumption. Through regular energy reviews, MUST can identify and reduce energy waste, improve overall energy efficiency, and continuously promote sustainable development. Furthermore, MUST explicitly adheres to the principles of green investment and environmental protection, has established a sustainable investment policy, and promotes green building projects. MUST will continue to invest in renewable energy facilities and actively conduct research and courses related to environmental protection.
Regarding Investment in Carbon-Intensive Energy Industries
MUST has clearly established a policy to avoid investment in carbon-intensive energy industries (particularly the coal and oil sectors). The MUST Fund commits to not investing in energy industries associated with high carbon emissions and environmental pollution, ensuring that all investment projects comply with the principles of sustainable development and green energy. Through this policy, MUST is not only committed to promoting the realization of a low-carbon economy but also plays an active role in advancing the energy transition and environmental protection. Additionally, the MUST Fund will further strengthen its efforts in green investment, prioritizing investment opportunities that support renewable energy, green technology, low-carbon technology, and other environmental projects. In the future, the MUST Fund will continue to review and optimize its investment portfolio, ensuring that investment decisions consistently align with global environmental standards and best practices for climate change response. MUST's green investment policy not only complies with national and international climate action goals but also reflects the university's commitment to environmental protection and social responsibility.
Technology Research, Development and Community Promotion
Urban Solid Waste to Green Hydrogen Technology: In 2024, MUST, as the Macau lead unit, participated in the national key research and development project "Technology Development and Integrated Demonstration of Distributed Co-generation of Green Electricity and Green Hydrogen from Macau Urban Solid Waste Sources." This project aims to convert Macau's increasing urban solid waste into green hydrogen and electricity, which is of direct significance for Macau to achieve energy structure adjustment and its "dual carbon" goals. Once the technology matures, it is expected to be promoted and applied at the community level. (Details: https://h2.in-en.com/html/h2-2435143.shtml)
Photovoltaic Power Generation Carbon Reduction Research: In 2024, the Macau Environment Research Institute of the MUST School of Innovation Engineering published research findings in the journal *Solar Energy* on the lifecycle carbon emissions of distributed photovoltaic systems, including an analysis of a local Macau case. This type of research provides important data support and scientific basis for promoting solar energy in Macau communities and households, helping the public understand the actual emission reduction benefits of clean energy.
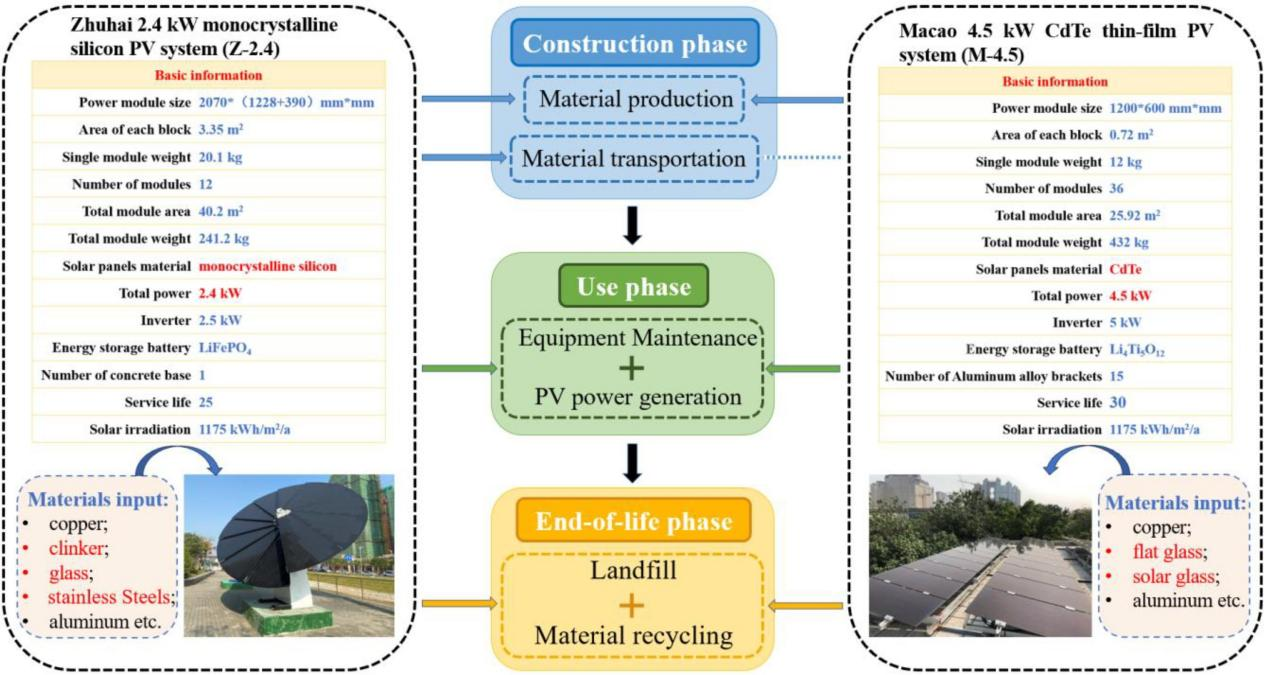
Dong L, Gu Y, Cai K, et al. Unveiling lifecycle carbon emissions and its mitigation potentials of distributed photovoltaic power through two typical case systems[J]. Solar Energy, 2024, 269: 112360.
Campus Practices and Self-Construction
MUST has developed its campus into a physical demonstration of sustainable development, interpreting green concepts to the community through practical actions. The university has set a clear goal to achieve campus carbon neutrality by 2039 and is systematically advancing various initiatives. In terms of hardware facilities, the campus has built one of the largest solar carports in Macau, equipped with 2,657 solar panels capable of producing significant clean electricity annually, with plans to further promote applications like solar glass windows. In daily operations, the university continuously participates in and organizes diverse energy-saving activities such as "Casual Summer, Let's Save Energy" and "Lights Off Hour," effectively reducing campus carbon emissions. These campus practices, which combine ambitious goals, technological application, and behavioral advocacy, form a vivid case study demonstrating the importance of energy efficiency and clean energy to students, staff, and the community.
 (Details: https://www.must.edu.mo/id-13630/article/view/id-35398.html?locale=zh_CN)
(Details: https://www.must.edu.mo/id-13630/article/view/id-35398.html?locale=zh_CN)
MUST Assists Government in Formulating Clean Energy and Energy Efficiency Technology Policies
Research jointly published by the Macau Environmental Research Institute of MUST, the Macau School of Systems Engineering, the School of Materials and Energy of Guangdong University of Technology, and the Guangzhou Institute of Energy Conversion, Chinese Academy of Sciences, titled "The potential challenge for the effective GHG emissions mitigation of urban energy consumption: A case study of Macau," for the first time used the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) method to systematically estimate the full lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions of Macau's urban energy consumption. This study conducted an in-depth analysis of the main emission sources of Macau's urban energy consumption, developed a balanced framework diagram for energy-related GHG emissions, and proposed effective emission reduction measures through scenario analysis.
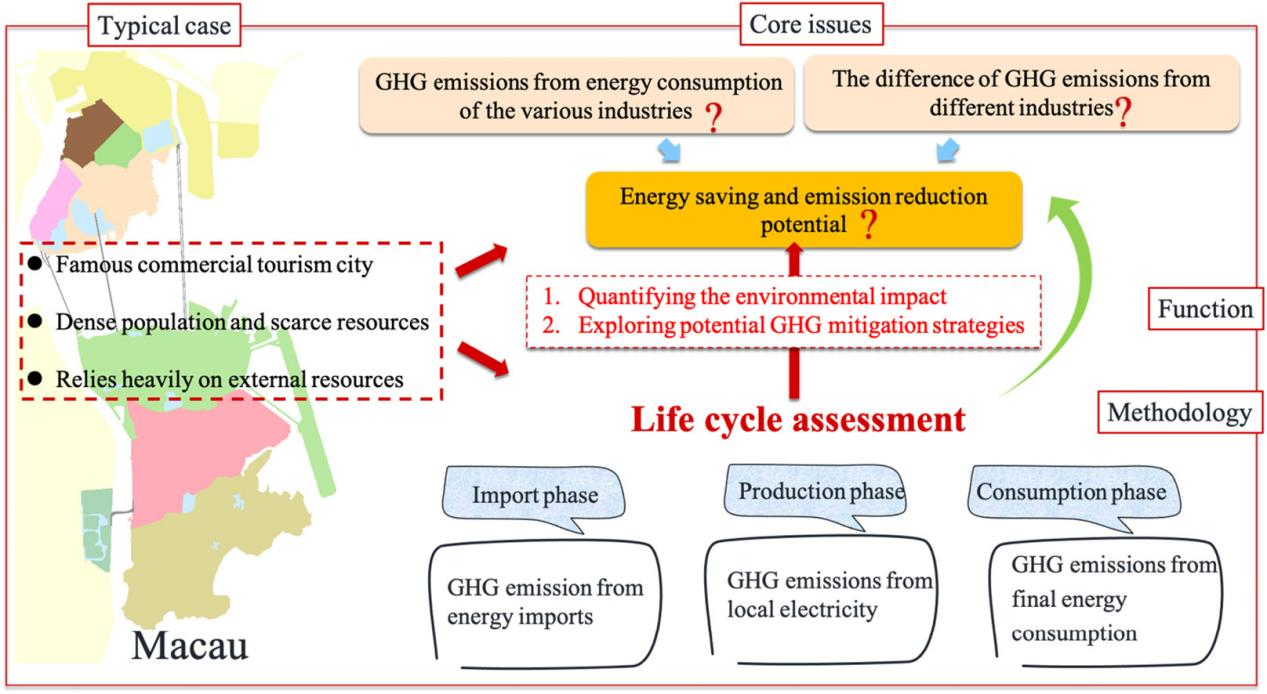
Through this research, MUST provided a scientific basis for the government's GHG emission reduction efforts, helping to identify and evaluate key emission sources in Macau's urban energy consumption and proposing feasible reduction strategies. These research results offer strong support for the Macau government in formulating policies related to clean energy, energy-saving technologies, and promoting green, low-carbon development. Simultaneously, MUST remains committed to promoting the formulation and implementation of sustainable development policies through interdisciplinary research and technological innovation, actively responding to the national "dual carbon" goals and assisting Macau in achieving a green, low-carbon transition.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0195925521001670?via%3Dihub)
MUST Supports the Development of Low-Carbon Technology Startups
Research jointly published by the MUST School of Innovation Engineering, the Energy Research Institute of China Huaneng Group Co., Ltd., and the Zhuhai MUST Science and Technology Research Institute, titled "Recommendations for the Development of the Hydrogen Energy Industry in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area based on SWOT and Analytic Hierarchy Process," delves into how the Greater Bay Area, as a key strategic region for China's hydrogen energy industry development, can promote high-level development of the hydrogen energy industry within the region and provide crucial support for achieving the "dual carbon" goals by constructing a comprehensive hydrogen industry assessment system.
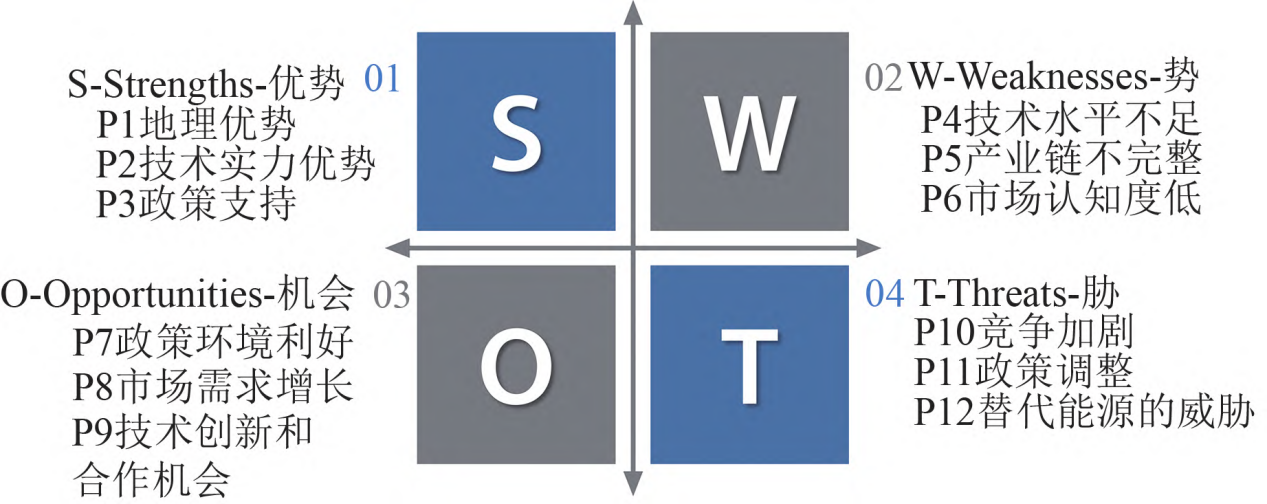
CHEN Jiarui, WU Jiaxuan, ZHOU Guopeng, KANG Junjie, SONG Qingbin. Proposals for the Development of Hydrogen Energy Industry in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area Based on SWOT Analytical Method and Hierarchical Analysis Approach[J]. Power Generation Technology.
The research focuses on the main factors affecting the development of the hydrogen energy industry and proposes comprehensive policy recommendations aimed at promoting the industry's steady development. These recommendations not only provide a scientific basis for government policy formulation but also offer strong support for low-carbon technology startups. Through in-depth analysis of the hydrogen industry, the research provides valuable guidance for startups in areas such as technological innovation, market positioning, and industrial chain integration, helping them find new development opportunities during the low-carbon economic transition.
MUST remains committed to promoting research and innovation in green technology, providing comprehensive support for low-carbon technology startups, and assisting them in gaining prominence in the global low-carbon economy.
Low-carbon Energy Use
Macau University of Science and Technology Promotes Services for Energy Efficiency Improvement and Low-Carbon Development
In response to the national "dual carbon" goals, MUST actively provides services related to energy efficiency improvement and low-carbon development to local industries. For example, at the "Enhancing Building Energy Efficiency, Facilitating Low-Carbon Development" international seminar, experts and scholars from Mainland China, Japan, and Macau shared cutting-edge technologies and experiences in reducing carbon emissions and improving energy efficiency in the construction sector. Through this seminar, MUST not only showcased its research achievements in building energy efficiency and carbon reduction but also provided professional support to industries in Macau and the Greater Bay Area regarding whole-lifecycle carbon reduction in buildings, energy efficiency assessment, and green building design. The university will continue to host similar events and, through research, technical consultation, and cooperation, promote the green, low-carbon transition of local industries and the construction sector, contributing to sustainable development.
(Details: https://www.must.edu.mo/cn/news/51675-article0602102048-c)